Radioactive Decay
In nature, there are a large number of atomic nuclei that can spontaneously emit elementary particles or nuclear fragments. Such a phenomenon is called radioactive decay. This effect was studied at the turn of 19−20 centuries by Antoine Becquerel, Marie and Pierre Curie, Frederick Soddy, Ernest Rutherford, and other scientists. As a result of the experiments, F.Soddy and E.Rutherford derived the radioactive decay law, which is given by the differential equation:
where \(N\) is the amount of a radioactive material, \(\lambda\) is a positive constant depending on the radioactive substance. The minus sign in the right side means that the amount of the radioactive material \(N\left( t \right)\) decreases over time (Figure \(1\)).
The given equation is easy to solve, and the solution has the form:
To determine the constant \(C,\) it is necessary to indicate an initial value. If the amount of the material at the moment \(t = 0\) was \({N_0},\) then the radioactive decay law is written as
Further, we introduce two useful parameters that follow from the given law.
The half life or half life period \(T\) of a radioactive material is the time reguired to decay to one-half of the initial value of the material. Hence, at the moment \(T:\)
The formula for the half life follows from here:
The average lifetime \(\tau\) of a radioactive atom is given by
As it can be seen, the half life \(T\) and the average lifetime \(\tau\) are related to each other by the formula:
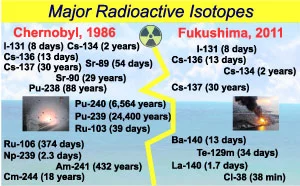
These \(2\) parameters vary widely for different substances. For example, the half life of Polonium-\(212\) is less than \(1\) microseconds, but the half life of Thorium-\(232\) is more than 1 billion years. A wide range of isotopes with different half lives was thrown from the atomic reactors and cooling pools in Chernobyl and Fukushima disasters (Figure \(2\)).
Solved Problems
Example 1.
Find the mass of a radioactive isotope if \(3\) half lives occurred. The initial mass of the material was \(80\,\text{g}.\)
Solution.
The mass of a radioactive material decreases as a result of decay twice after each half life. So, after \(3\) half lives the quantity of the material will be \({\left( {\frac{1}{2}} \right)^3} = {\frac{1}{8}}\) of the initial amount. Hence, the mass after decay is \(80\,\text{g}\cdot {\frac{1}{8}} = 10\,\text{g}.\)
Example 2.
The initial mass of an Iodine isotope was \(200\,\text{g}.\) Determine the Iodine mass after \(30\) days if the half life of the isotope is \(8\) days.
Solution.
According to the radioactive decay law the mass of an isotope depends on time as follows:
Here the decay constant \(\lambda\) is equal to
Calculate the mass of the Iodine isotope in \(30\) days: